File-System Structure
File system reside on secondary storage (disk)
File control block (FCB) : storage structure consisting of information about a file
Device driver controls the physical device
Layered File System
Device driver manage I/O devices at the I/O control layer
Basic file system : given command like "retrieve block 1" translates to device driver
manages memory buffer and caches
File organization module : understands file, logical address, and physical blocks
translates logical block # to physical block #, manages free space, disk allocation
Logical file system : manages metadata information
translates file name into file number, file handle, location by maintaining file control blocks (inodes in UNIX)
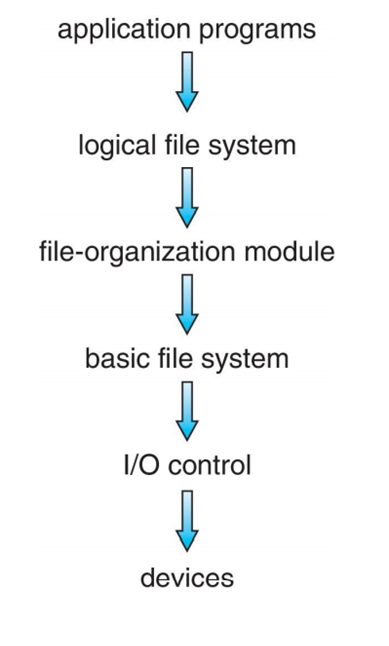
Layering useful for reducing complexity and redundancy, but adds overhead and can decrease performance
File-System Operation
On-disk and in-memory structures
Boot control block : contains info needed by system to boot Operating System
Volume control block : contains volume details (total # of blocks, # of free blocks ...)
File control block : contains many details many details about the file (inode number, permissions, size, dates ...)
In-Memory File System Structures
Mount table : stores file system mouts, mount points, file system types
System-wide open-file table : contains a copy of the FCB of each file and other info
Per-process open-file table : contains pointers to appropriate entries in system-wide open-file table as well as other info

Directory Implementation
Linear list : file name with pointer to the data blocks
Hash table : linear list with hash data structure
Decreases directory search time
collisions : situations where two file names hash to the same location
Allocation Methods
Contiguous allocation : each file occupies set of contiguous blocks
simple (only starting location (block #) and length (number of blocks) are required)

Linked allocation : each file a file a linked list of blocks
No external fragmentation, No compaction
Reliability can be a problem

FAT (File Allocation Table) : begining of volume has table, indexed by block number
much like a linked list, but faster on disk and cacheable
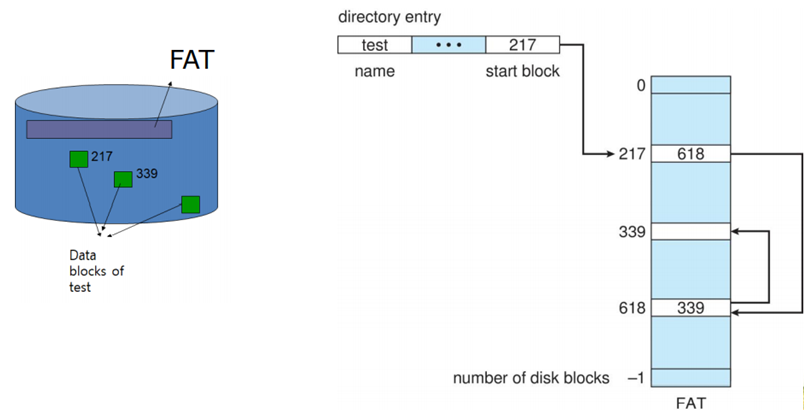
Indexed allocation : Each file has its own index block of pointer to its data blocks
Free-space management
File system maintains free-space list to track available blocks/clusters
Bit vector or bitmap (bit[i] = 1 => free, bit[i] = 0 => occupied)
Linked free space list on disk : cannot get contiguous space easily, no waste of space
Groupging : modify linked list to store address of next n-1 free blocks in first free block, plus a pointer to next block
Counting : keep address of first free block and count of following free blocks
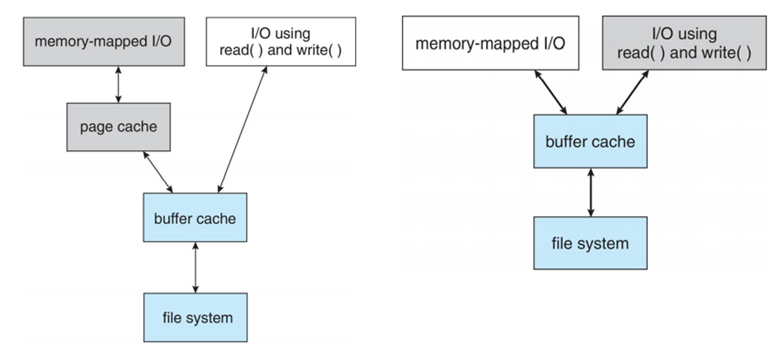
Page Cache
A page cache caches pages rather than disk blocks using virtual memory techniques and addresses
Unified Buffer Cache
Unified buffer cache uses the same page cache to cache both memory-mapped pages and ordinary file system I/O to avoid double caching
Recovery
Files and directories are kept both in main memory and on disk
File system can be crashed for various reasons (System crach, bugs in file-system implementation, disk controller...)
Deal with methods to recover the file system on crash (consistency checking, log structrued file system)
Log structured file system : log structured file systems record each metadata update to the file system as a transaction
'Operating System Design' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Operating System Design - Processes (0) | 2021.06.17 |
|---|---|
| Operating System Design - Operating System Structures (0) | 2021.06.16 |
| Operating System Design - I/O Systems (0) | 2021.06.16 |
| Operating System Design - Virtual Memory (0) | 2021.06.15 |
| Operating System Design - Main Memory (0) | 2021.06.15 |


